
The right resources for you and your patients
Starting on a new product or treatment can be difficult. Find the tools you need to train and guide your patients into to good management routines.
Introduction to Peristeen® Plus Transanal Irrigation for Healthcare Professionals
Get an animated insight into how the digestive system works and learn more about bowel irrigation as a technique to help your patients empty their bowels. Watch the effect that transanal irrigation has on the bowels visualized by means of scinitigraphic imaging of the colon.
The benefits of using Peristeen® Plus:
- Prevents faecal incontinence and constipation, for up to two days between irrigations
- Enables the patient to decide when to empty their bowels, so it fits in with their lifestyle
- Improves quality of life
- Reduces the total time spent daily by the patient on their bowel management
WheelMate - Find accessible toilets and parking near you
Finding clean, accessible restrooms and parking can be a challenge. The WheelMate app is a simple way to find restrooms and parking spaces on the go. Whether you’re local or traveling, WheelMate helps you plan your day. Learn more below.
Frequently asked questions about bowel irrigation
This FAQ is intended as a guide to commonly asked questions. Please always consult your healthcare professional regarding bowel irrigation.
For more information, watch the video about getting started with Peristeen® Plus.
What is bowel irrigation?
Bowel irrigation is where water is introduced into the bowel using a rectal catheter. The water stimulates the bowel and flushes out the stool, leaving the lower half of the bowel empty. It is important to do it regularly to prevent constipation and the risk of bowel accidents. Read more about Coloplast’s bowel irrigation system, Peristeen®Plus
Where can I get Peristeen® Plus?
In order to use Peristeen Plus, you need to get a referral from your GP, specialist, or nurse. You must also always consult an experienced specialist healthcare professional before starting up the irrigation procedure and you must receive thorough instruction from a healthcare professional before using this product.
How often should I irrigate?
Most people start with irrigating every day. It takes approximately 3 months to establish a regular routine. Once you have an established routine, irrigating every other day may work well. With time and practice you will find out what works best for you. What is important, is to remember to irrigate regularly to prevent constipation and minimise the risk of bowel accidents. Always ask your doctor or nurse for advice.
What time of the day is best for irrigating?
Try to get into a routine where you irrigate around the same time of the day. Eating and drinking helps the bowel’s natural movement, so about 30 minutes after a meal is a good time. But do not be afraid to change the routine slightly to suit your day-to-day routine.
Can I travel with the irrigation equipment?
Yes – remember to bring your irrigation system along with lots of disposable catheters as they may not sell them everywhere. If you are going to use the system abroad, use bottled or cooled boiled water in places where the tap water is not safe to drink. Remember in different time zones your body may take a while to get used to a new routine. You may also be eating different types of food, which can affect the bowels.
What should I do if I leak between irrigations?
If you experience bowel leakage between irrigations, it may be due to insufficient emptying of your bowel due to constipation or hard stool. Alternatively, you may be using too much water during irrigation. Contact your doctor or nurse to help you adapt to your bowel plan. A Peristeen® Anal Plug may help if the problem persists.
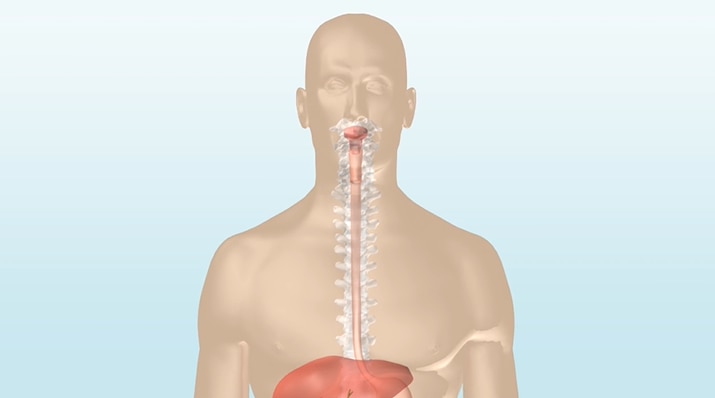
How the bowel works
The bowel is divided into the small intestine and the large intestine (colon, rectum and anus). The main function of the small intestine is to absorb nutrients released from the food digested in the stomach. The large intestine absorbs water from food and forms semi-solid and solid food waste into stools, which are eliminated from the body through the anus. Waste product is moved along the digestive system by a wave of involuntary contractions (peristalsis).

Bowel Symptoms
Bowel symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause. Read about the most common bowel problems people are experiencing and test your patients bowel symptoms.
What is neurogenic bowel?
Neurogenic bowel can be described as slow movement of stools, constipation, bowel leakage, and difficulty emptying the bowel. Control of the external anal sphincter muscles may also be disrupted, increasing the risk of bowel accidents.
There are two main types of neurogenic bowel dysfunction:
- Reflex bowel
- Flaccid bowel
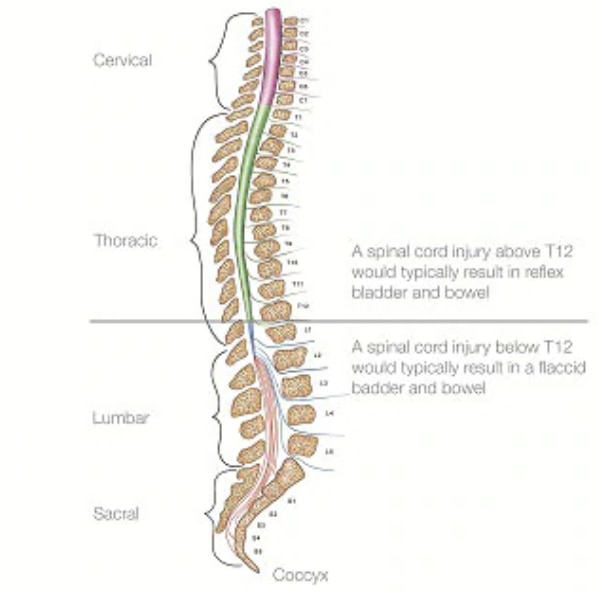
Reflex bowel
Reflex bowel causes loss of the ability to feel when the bowel is full. Although the anal sphincter muscle (the muscle that keeps the anus closed) remains tight, it will open on a reflex basis when the rectum becomes full and, therefore, the bowel can empty at any time unless appropriately managed. Reflex bowel can occur when the spinal cord is damaged above the T12 level.
Flaccid bowel
Flaccid bowel is when the anal sphincter muscle (that normally keeps the anus closed) becomes relaxed and stays open, often leading to accidental emptying of the bowel. Flaccid bowel is generally caused by damage below the T12 level.
One cause of neurogenic bowel is spinal cord injury (SCI). The impact on bowel function depends on the level of spinal cord injury and where the damage occurs (as mentioned above).
Other possible causes of neurogenic bowel include multiple sclerosis, spina bifida and Parkinson’s disease.
